상속은 클래스가 다른 클래스의 속성과 메소드를 그대로 받아오는 것이고, 다형성은 같은 이름의 메소드가 다른 행동을 할 수 있게 하는 것이다.
상속을 활용하면, 코드의 재사용성을 높이고, 중복을 줄이고
다형성을 활용하면, 동일한 인터페이스에 대해 다양한 구현을 제공할 수 있어 코드의 유연성이 증가한다.
- 다형성은 주로 메소드 오버라이딩(overriding)이나 오버로딩(overloading)을 통해 구현되며, 각각 메소드 오버라이딩은 하위 클래스가 상위 클래스의 메소드를 재정의하고 오버로딩은 같은 이름의 메소드가 매개변수의 유형이나 개수에 따라 다른 동작을 하는 것을 의미한다.
상속
- 키워드
base, this
base 는 상위 클래스 객체를 의미
this 는 해당 객체(하위클래스) 를 의미
ex)
생성자() : this() <- 하위클래스의 다른 생성자를 호출
생성자() : base() <- 상위 클래스의 생성자를 호출
: 오른쪽의 인자가 생성자의 파라미터로 대입 된다.
base.X 상위클래스의 X
this.Z 하위클래스의 Z
namespace practice;
using System;
public class Point
{
public int X { get; set;}
public int Y { get; set;}
public Point(int x, int y)
{
X = x;
Y = y;
}
// public Point(int x, int y) => (X, Y) = (x, y); // 상단과 동일한 작업 [ C# 7.0 이상에서 도입된 튜플 대입 방식 ]
}
public class Point3D : Point
{
public int Z { get; set; }
// 기존 생성자
public Point3D(int x) : this(x, 0, 0)
{ // Point3D(3)
}
public Point3D(int x, int y) : this(x, y, 0)
{ // Point3D(4, 5)
}
public Point3D(string x, string y) : this(Convert.ToInt32(x), Convert.ToInt32(y), 0)
{ // Point3D("6", "7")
}
public Point3D(int x, int y, int z) : base(x, y)
{ // Point3D(8, 9, 10)
this.Z = z; // 하위클래스(Point3D)의 int Z 를 사용하겠다고 명시적으로 표시 this
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Point a = new Point(1, 2);
Point3D b = new Point3D(3);
Point3D c = new Point3D(4, 5);
Point3D d = new Point3D("6", "7");
Point3D e = new Point3D(8, 9, 10);
// 결과 출력
Console.WriteLine($"A: {a.X}, B: {a.Y}"); // 출력값 : A: 1, B: 2
Console.WriteLine($"A: {b.X}, B: {b.Y}, Z: {b.Z}"); // 출력값 : A: 3, B: 0, Z: 0
Console.WriteLine($"A: {c.X}, B: {c.Y}, Z: {c.Z}"); // 출력값 : A: 4, B: 5, Z: 0
Console.WriteLine($"A: {d.X}, B: {d.Y}, Z: {d.Z}"); // 출력값 : A: 6, B: 7, Z: 0
Console.WriteLine($"A: {e.X}, B: {e.Y}, Z: {e.Z}"); // 출력값 : A: 8, B: 9, Z: 10
}
}
다형성
상위 클래스의 멤버함수인 Draw()함수
[ public virtual void Draw() ] << virtual 을 꼭 붙여야 한다.
하위 클래스에서 상위클래스의 멤버함수를 재정의(오버라이딩) 함
[ public override void Draw() ] << 오버라이딩시 override 를 꼭 붙여 줘야한다.
<< 하위클래스에서는 상위클래스의 virtual 함수를 정의하지 않아도 된다.
namespace practice;
using System;
public class Shape
{
// A few example members
public int X { get; private set; }
public int Y { get; private set; }
public int Height { get; set; }
public int Width { get; set; }
// Virtual method
public virtual void Draw()
{
Console.WriteLine("Performing base class drawing tasks");
}
}
public class Circle : Shape
{
public override void Draw()
{
// Code to draw a circle...
Console.WriteLine("Drawing a circle");
base.Draw();
}
}
public class Rectangle : Shape
{
public override void Draw()
{
// Code to draw a rectangle...
Console.WriteLine("Drawing a rectangle");
base.Draw();
}
}
public class Triangle : Shape
{
// 하위클래스에서는 상위클래스의 virtual 함수를 정의하지 않아도 된다.
// public override void Draw()
// {
// // Code to draw a triangle...
// Console.WriteLine("Drawing a triangle");
// base.Draw();
// }
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
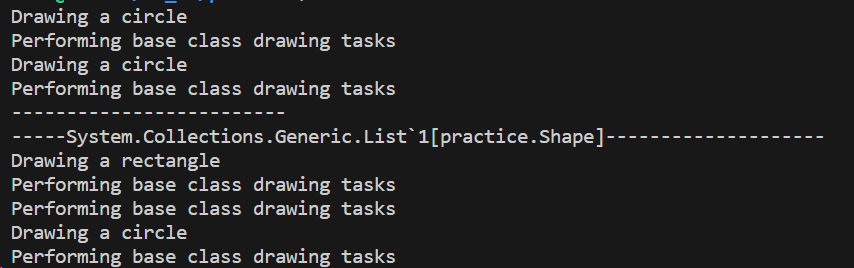
Shape C_S = new Circle();
Circle C_S_2 = new Circle();
C_S.Draw();
C_S_2.Draw();
Console.WriteLine("-------------------------");
var shapes = new List<Shape>
{
new Rectangle(),
new Triangle(),
new Circle()
};
Console.WriteLine($"-----{shapes}--------------------");
foreach (var shape in shapes)
{
shape.Draw();
}
}
}
'언어 정리 > C# 개념 및 lib' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 참조자, static method, 오버라이딩, 오버로드 (1) | 2024.01.09 |
|---|---|
| 구조체, 인터페이스, 열거형(enum), 튜플, 네임드튜플, 딕셔너리, Nullable (0) | 2024.01.09 |
| 생성자 (0) | 2024.01.09 |
| var, foreach, List 자료형 (0) | 2024.01.08 |
| if 문 for 문 while 문 (0) | 2024.01.08 |



댓글